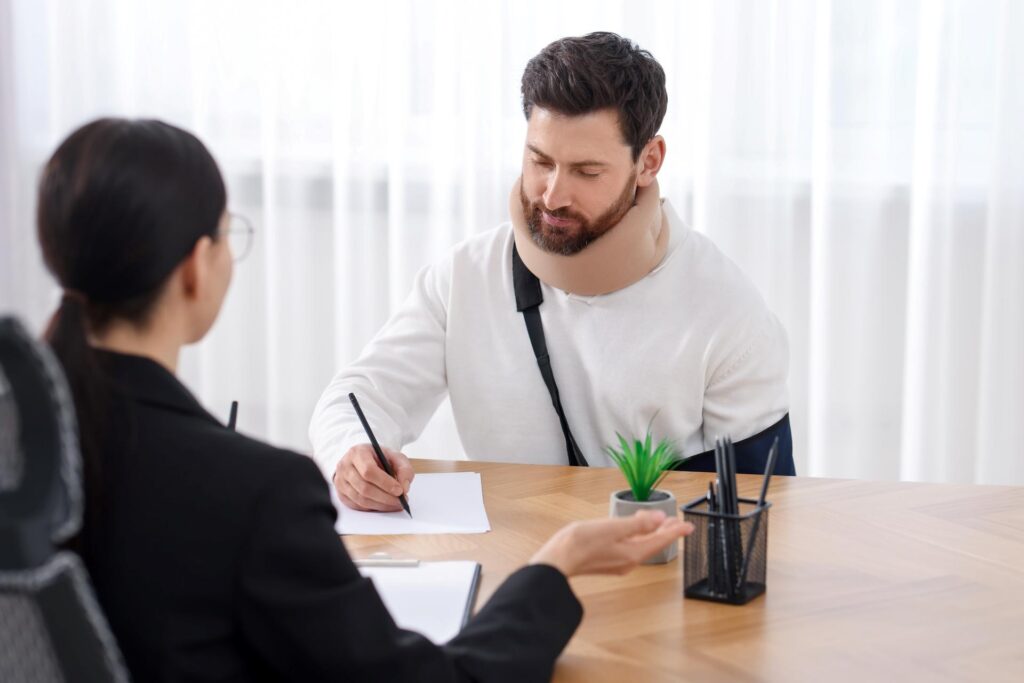
Premises liability is a fundamental aspect of personal injury law, ensuring property owners and occupiers are responsible for maintaining a safe environment. When someone is injured on another person’s property due to hazardous conditions, the property owner may be held legally accountable under certain circumstances. Understanding the key factors that contribute to premises liability is vital for determining the validity of a claim and clarifying the obligations of property owners. This article delves into the common elements that shape premises liability cases and examines their broader legal and practical implications.
The Duty of Care
Premises liability revolves around the principle of “duty of care,” which requires property owners or occupiers to maintain a reasonably safe environment for visitors. The scope of this duty, however, varies based on the visitor’s legal classification. Visitors are typically categorized as invitees, licensees, or trespassers, with each group entitled to a different level of care. For example, invitees—such as customers in a store—are owed the highest standard of care, as they are on the property for the benefit of the owner or occupier. In contrast, trespassers are generally owed only a minimal duty of care, though exceptions exist, particularly in cases involving children or hazardous conditions.
Knowledge of Hazardous Conditions
One essential factor in premises liability cases is whether the property owner was aware of the dangerous condition that caused the injury. Liability typically arises if the owner either knew about the hazard or should have reasonably known about it but failed to address it appropriately. For example, if a spill in a grocery store goes unnoticed and a customer slips and falls, the store’s failure to inspect and address safety hazards may result in liability.
Negligence in Addressing Hazards
Even if a property owner is aware of a dangerous condition, liability largely depends on whether they took reasonable steps to mitigate the risk. A failure to provide proper warnings or repairs in a timely manner can be viewed as negligence. For example, leaving a broken handrail on a staircase unrepaired despite knowing it poses a safety risk can lead to significant injuries and a corresponding claim. On the other hand, if the property owner took clear and reasonable actions, such as placing warning signs or scheduling repairs promptly, it may reduce or eliminate their liability.
The Role of the Injured Party
The actions of the injured party often play a significant role in premises liability cases. Courts typically examine whether the injured individual acted in a way that contributed to their own injury. This is referred to as “comparative negligence” in legal terms. For instance, if an individual ignored a clearly posted warning or failed to exercise reasonable care under the circumstances, their ability to recover damages may be reduced or denied.
Types of Hazards Commonly Associated with Premises Liability
Premises liability claims arise from various hazards, ranging from slip-and-fall accidents to inadequate property security. Common examples include wet floors, uneven sidewalks, faulty electrical wiring, inadequate lighting, or unsecured structures. Each situation is assessed based on the circumstances, including the property’s use, the foreseeability of harm, and the measures taken by the owner to prevent injuries. Cases involving poor security measures, such as failing to install locks or alarms in high-risk areas, may also result in liability if a person suffers harm as a result of criminal activities on the property.
Legal Outcomes and Implications
The success of premises liability cases hinges on proving that a property owner’s negligence directly led to the injury. To build a strong claim, plaintiffs must typically show that the owner had a duty of care, failed to fulfill that duty, and that this failure caused tangible harm. When successful, such claims can secure compensation for medical bills, lost income, and other damages resulting from the injury.
For property owners, premises liability emphasizes the importance of diligent maintenance, proactive risk management, and compliance with safety standards. Failure to uphold these responsibilities not only endangers visitors but also exposes property owners to potential legal and financial consequences. On the other hand, for individuals visiting a property, awareness and caution can play a critical role in preventing accidents.
Premises liability is a multifaceted area of law that demands a thorough assessment of circumstances, responsibilities, and actions. Understanding the core factors that influence premises liability empowers property owners to create safer environments and helps injured individuals better comprehend their legal rights. Whether you are a property owner or a visitor, a clear appreciation of premises liability can serve as a foundation for ensuring safety and accountability in daily interactions with physical spaces. Contact our team today to learn more.